Home > Articles > Programming > C/C++
- Mobject1 = new MyObject1(this), mobject2 = new MyObject2(this); connect(mobject1, SIGNAL(valueChanged), mobject2, SLOT(printNumber)); (2)QMLと接続できる CのシグナルをQMLのスロットで受けたり、QMLのシグナルをCのスロットで受けることが可能です。.
- Both options are explained in the Qt Tutorial. Also, you need to use a QVariant in order to exchange data between C and QML. You can also register types, e.g. Widgets and stuff, so that you can use them in QML as a “native” type like a rectangle.
Qt Signal Slot With 2 Arguments
- Signals and Slots in Depth
Support for Signals and Slots¶ One of the key features of Qt is its use of signals and slots to communicate between objects. Their use encourages the development of reusable components. A signal is emitted when something of potential interest happens. A slot is a Python callable. If a signal is connected to a slot then the slot is called when the signal is emitted.
This chapter is from the book
This chapter is from the book
Signals and Slots in Depth
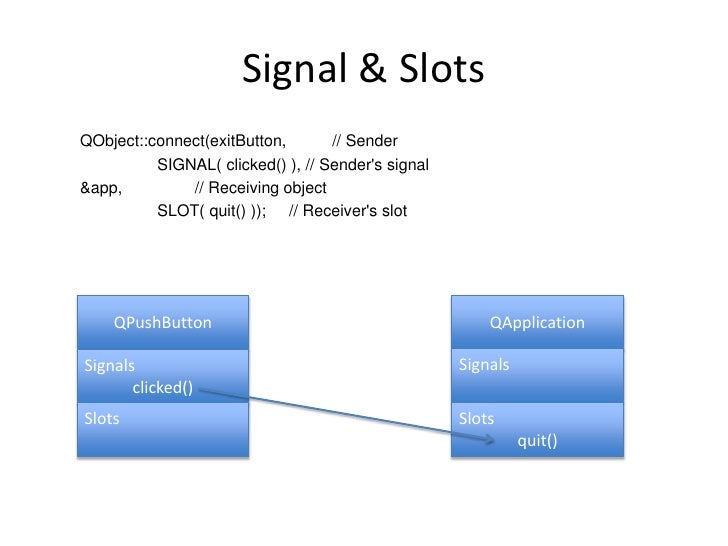
The signals and slots mechanism is fundamental to Qt programming. It enables the application programmer to bind objects together without the objects knowing anything about each other. We have already connected some signals and slots together, declared our own signals and slots, implemented our own slots, and emitted our own signals. Let's take a moment to look at the mechanism more closely.
Slots are almost identical to ordinary C++ member functions. They can be virtual; they can be overloaded; they can be public, protected, or private; they can be directly invoked like any other C++ member functions; and their parameters can be of any types. The difference is that a slot can also be connected to a signal, in which case it is automatically called each time the signal is emitted.
The connect() statement looks like this:
where sender and receiver are pointers to QObjects and where signal and slot are function signatures without parameter names. The SIGNAL() and SLOT() macros essentially convert their argument to a string.
In the examples we have seen so far, we have always connected different signals to different slots. There are other possibilities to consider.
One signal can be connected to many slots:
When the signal is emitted, the slots are called one after the other, in an unspecified order.
Many signals can be connected to the same slot:
When either signal is emitted, the slot is called.
A signal can be connected to another signal:
When the first signal is emitted, the second signal is emitted as well. Apart from that, signal–signal connections are indistinguishable from signal–slot connections.
Connections can be removed:
This is rarely needed, because Qt automatically removes all connections involving an object when that object is deleted.
To successfully connect a signal to a slot (or to another signal), they must have the same parameter types in the same order:
Exceptionally, if a signal has more parameters than the slot it is connected to, the additional parameters are simply ignored:
If the parameter types are incompatible, or if the signal or the slot doesn't exist, Qt will issue a warning at run-time if the application is built in debug mode. Similarly, Qt will give a warning if parameter names are included in the signal or slot signatures.
So far, we have only used signals and slots with widgets. But the mechanism itself is implemented in QObject and isn't limited to GUI programming. The mechanism can be used by any QObject subclass:
Notice how the setSalary() slot is implemented. We emit the salaryChanged() signal only if newSalary != mySalary. This ensures that cyclic connections don't lead to infinite loops.
Related Resources

- Book $31.99
Qt Signal Slot Parameter
- Book $35.99
Qt Signal Slots
- Book $43.99